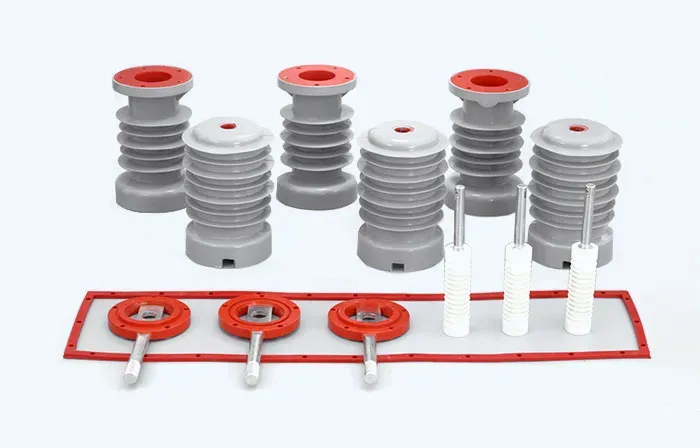
High Voltage Insulators serve a critical role in power systems by preventing electrical leakage and ensuring that electricity flows safely along transmission lines. These insulators are designed to withstand extreme weather conditions, high voltages, and mechanical stress. They are typically made from materials such as porcelain, glass, or composite polymers, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages.
Core Functions of High Voltage Insulators
The primary function of High Voltage Insulators is to isolate electrical conductors from the ground and other structures. This isolation is essential for preventing short circuits and ensuring that electricity travels along the intended path. Additionally, insulators help to support the weight of the conductors and maintain the necessary spacing between them, which is crucial for safety and efficiency.
Selecting the Right High Voltage Insulator
When it comes to selecting High Voltage Insulators, several factors should be considered:
•Voltage Rating: Ensure that the insulator can handle the maximum voltage of your system. This is critical for preventing breakdowns and ensuring safety.
• Environmental Conditions: Consider the local climate and environmental factors. For example, areas with high pollution levels may require insulators that are more resistant to contamination.
•Mechanical Strength: Assess the mechanical stresses that the insulators will face, such as wind loads or ice accumulation. Choosing insulators with adequate mechanical strength is vital for long-term reliability.
•Material Type: Each material has its own set of properties. Porcelain is known for its durability, while composite materials offer lightweight options with excellent performance in harsh conditions.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance of High Voltage Insulators is essential to ensure their longevity and performance. Here are some best practices:
•Visual Inspections: Conduct routine visual inspections to check for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Look for cracks, chips, or any buildup of dirt and grime.
•Cleaning: In areas with high pollution or salt exposure, cleaning insulators can help maintain their performance. Use appropriate cleaning methods to avoid damaging the insulator surface.
• Testing: Implement regular electrical testing to assess the insulator's performance. This can help identify potential issues before they lead to failures.
Emerging Trends in High Voltage Insulators
The industry is witnessing several emerging trends that could shape the future of High Voltage Insulators:
• Smart Insulators: The integration of sensors and monitoring technology into insulators is becoming more common. These smart insulators can provide real-time data on their condition, helping to predict failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
•Sustainability: As the focus on sustainability grows, manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and production methods for insulators. This shift not only benefits the environment but can also lead to improved performance.
•Advanced Materials: Research into new materials, such as nanocomposites, is ongoing. These materials may offer enhanced properties, such as increased strength and resistance to environmental factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, High Voltage Insulators are a vital component of power transmission systems. Understanding their functions, making informed selections, and adhering to maintenance best practices can significantly enhance the reliability and safety of power systems.
As the industry evolves, staying updated on emerging trends will ensure that you are well-equipped to make the best choices for your power infrastructure. By prioritizing the quality and performance of High Voltage Insulators, we can contribute to a more efficient and safer energy future. The Core Functions of High Voltage Insulators You Can’t Ignore

 EN
EN