
High Voltage Inssulator are important electrical equipment in power transmission and distribution systems, usually used to support and isolate the potential difference between high-voltage conductors and the ground or other grounding structures. Made of advanced composite materials, they not only effectively resist erosion in harsh environments, but also have significant advantages such as light weight, dirt resistance, and easy maintenance. They are widely used in high-voltage transmission lines to ensure the safety and stability of power transmission.

As a key device for lightning protection of power systems, lightning arresters can effectively prevent the damage of lightning overvoltage to power equipment. By discharging lightning energy or limiting the overvoltage amplitude, they protect power equipment from lightning damage. Lightning arresters have the characteristics of fast response, high reliability, and long life, and can adapt to various severe weather conditions. They are widely used in transmission lines, substations, power plants and other places.

Metering box plays an important role in the power system, it is not only the power measurement tool, but also the power management and energy efficiency monitoring of the right hand. Through accurate measurement and real-time monitoring, the metering box helps to achieve stable operation of the power system, improve energy efficiency and reduce energy costs.

Low Voltage Insulator are important power equipment in low-voltage power systems. They are usually composed of insulating materials and supporting structures. Commonly used insulating materials include fiberglass, ceramics, rubber, etc., which have good insulation properties and mechanical strength. They effectively isolate the conductive parts, prevent short circuits and arc discharges, and ensure the safe and stable operation of the power distribution system. At the same time, they have good weather resistance and anti-aging properties, ensuring that they can still work reliably under extreme climatic conditions.

Cable accessories are indispensable connection and protection components in power cable systems, including cable terminals, heat shrink tubing, etc. High-quality insulating materials and advanced manufacturing technology are used to ensure safe connection and reliable operation of cable systems. They are widely used in urban power grids, industrial power distribution, rail transit and other fields, providing reliable connection and protection for power transmission and distribution.

As an important measurement and protection device in the power system, the current transformer can convert high voltage or large current into low voltage or small current for use in measuring instruments, relay protection and other equipment. Its high-precision and wide-range measurement characteristics ensure accurate monitoring of power system parameters. It adopts advanced magnetic circuit design and manufacturing technology, has excellent anti-saturation and anti-interference performance, and can operate stably in complex electromagnetic environments. Current transformers are widely used in substations, power plants and industrial distribution systems.

Epoxy resin tubes are made of high-quality epoxy resin materials and are formed through advanced processes. They have good temperature resistance, pressure resistance, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Their excellent insulation performance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength make them widely used in the fields of electricity, chemical industry, water treatment, etc. Epoxy resin tubes have a compact structure, smooth surface, and are easy to process and install, playing an important role in cable protection.
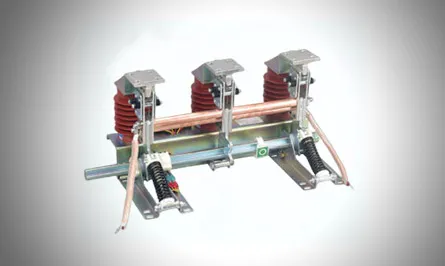
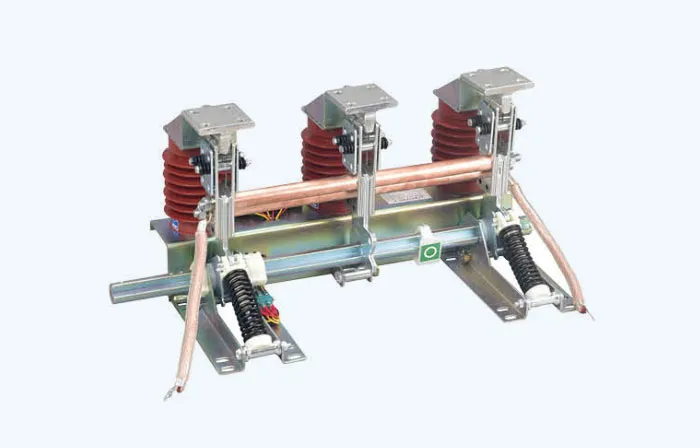
A grounding switch is a mechanical switch used in the grounding part of a circuit. It can carry current under abnormal conditions (such as short-circuit current) for a certain period of time, but it is not required to carry current under normal circuit conditions. A grounding switch has no arc extinguishing device. Its main functions include: replacing portable grounding wires, grounding high-voltage equipment and lines during maintenance to protect personal safety; creating artificial grounding to meet protection requirements.

An isolating switch is a device mainly used for isolating power sources, switching operations, and connecting and disconnecting small current circuits without arc extinguishing function. The main function of an isolating switch is to disconnect circuits without load current, so that the repaired equipment has a clear breakpoint with the power supply to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel. An isolating switch does not have a dedicated arc extinguishing device and cannot cut off load current and short circuit current, so it must be operated when the circuit is disconnected by the circuit breaker.
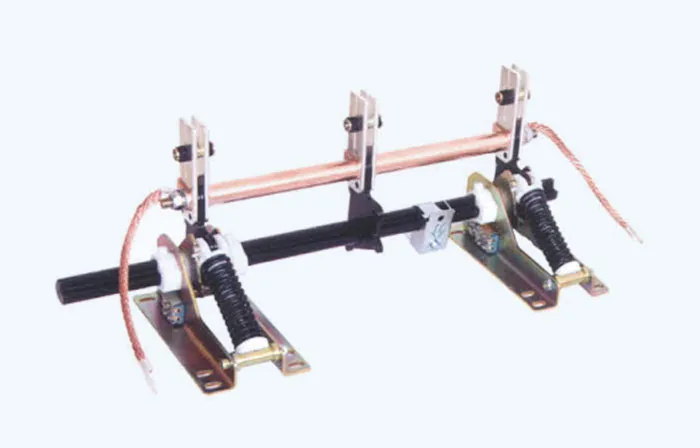

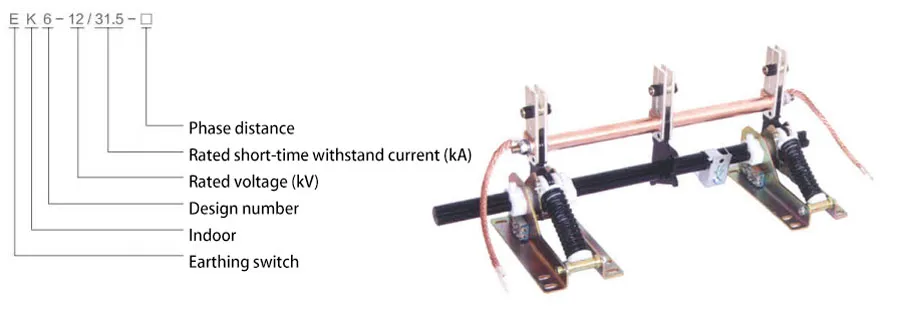
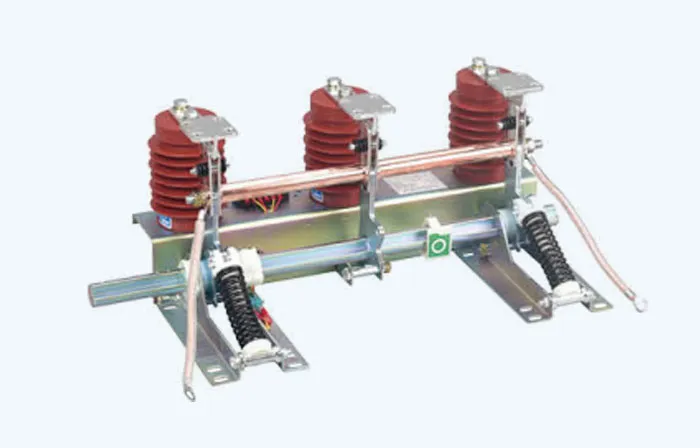
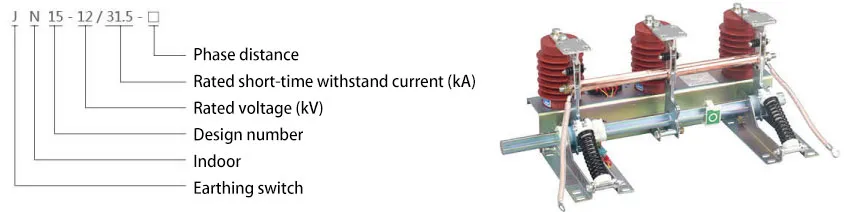
Commonly used insulation materials for Chundexin insulators include advanced composite materials, such as glass fiber, ceramics, rubber, etc., which have good insulation properties and mechanical strength. They can effectively isolate conductive parts, prevent short circuits and arc discharges, and ensure the safe and stable operation of power distribution systems.
Chundexin surge arresters are widely used in transmission lines, substations, power plants and other places.
Commonly used insulation materials for Chundexin insulators include advanced composite materials, such as glass fiber, ceramics, rubber, etc., which have good insulation properties and mechanical strength. They can effectively isolate conductive parts, prevent short circuits and arc discharges, and ensure the safe and stable operation of power distribution systems.
GET A QUOTE